- AI Platforms
 Fueled by a Visual Designer, Marketplace for Reusable Connectors, ETL & ML Blocks.
Fueled by a Visual Designer, Marketplace for Reusable Connectors, ETL & ML Blocks.
Agentic AI Integrations
Integration enables agents to deliver AI outcomes faster, better, simpler.
DataNimbus FinHub
With the DataNimbus FinHub platform, we offer a whole range of escrow management.Navigate Your AI Journey
Break free from legacy! Modernize your core with intelligent, AI-powered solutions
- AI Applications
- Services

DataNimbus Consulting
- Data AI Strategy
- Data and AI Architecture
- Payment Automation
Product Engineering Services
- Product Design & UX
- Custom APIs
- AI enabled Applications
Data Analytics & AI/ML
- Data Management
- AI Applications and Models
- Custom Workflows

Enterprise Integration
- Custom API
- Process Orchestration
- Intelligent Process Orchestration Management
- Customers
- Resources
- Company
- AI Platforms
 Fueled by a Visual Designer, Marketplace for Reusable Connectors, ETL & ML Blocks.
Fueled by a Visual Designer, Marketplace for Reusable Connectors, ETL & ML Blocks.
Agentic AI Integrations
Integration enables agents to deliver AI outcomes faster, better, simpler.
DataNimbus FinHub
With the DataNimbus FinHub platform, we offer a whole range of escrow management.Navigate Your AI Journey
Break free from legacy! Modernize your core with intelligent, AI-powered solutions
- AI Applications
- Services

DataNimbus Consulting
- Data AI Strategy
- Data and AI Architecture
- Payment Automation

Product Engineering Services
- Product Design & UX
- Custom APIs
- AI enabled Applications

Data Analytics & AI/ML
- Data Management
- AI Applications and Models
- Custom Workflows

Enterprise Integration
- Custom API
- Process Orchestration
- Intelligent Process Orchestration Management
- Customers
- Resources
- Company
- AI Platforms
 Fueled by a Visual Designer, Marketplace for Reusable Connectors, ETL & ML Blocks.
Fueled by a Visual Designer, Marketplace for Reusable Connectors, ETL & ML Blocks.
Agentic AI Integrations
Integration enables agents to deliver AI outcomes faster, better, simpler.
DataNimbus FinHub
With the DataNimbus FinHub platform, we offer a whole range of escrow management.Navigate Your AI Journey
Break free from legacy! Modernize your core with intelligent, AI-powered solutions
- AI Applications
- Services

DataNimbus Consulting
- Data AI Strategy
- Data and AI Architecture
- Payment Automation

Product Engineering Services
- Product Design & UX
- Custom APIs
- AI enabled Applications

Data Analytics & AI/ML
- Data Management
- AI Applications and Models
- Custom Workflows

Enterprise Integration
- Custom API
- Process Orchestration
- Intelligent Process Orchestration Management
- Customers
- Resources
- Company
- AI Platforms
 Fueled by a Visual Designer, Marketplace for Reusable Connectors, ETL & ML Blocks.
Fueled by a Visual Designer, Marketplace for Reusable Connectors, ETL & ML Blocks.
Agentic AI Integrations
Integration enables agents to deliver AI outcomes faster, better, simpler.
DataNimbus FinHub
With the DataNimbus FinHub platform, we offer a whole range of escrow management.Navigate Your AI Journey
Break free from legacy! Modernize your core with intelligent, AI-powered solutions
- AI Applications
- Services

DataNimbus Consulting
- Data AI Strategy
- Data and AI Architecture
- Payment Automation

Product Engineering Services
- Product Design & UX
- Custom APIs
- AI enabled Applications

Data Analytics & AI/ML
- Data Management
- AI Applications and Models
- Custom Workflows

Enterprise Integration
- Custom API
- Process Orchestration
- Intelligent Process Orchestration Management
- Customers
- Resources
- Company
Blog
Event-Driven vs. Batch Processing: Choosing the Right Approach for Your Data Platform
Introduction:
In today’s data-driven world, platforms must efficiently process and analyze vast amounts of information to deliver actionable insights. Real-time data processing has gained prominence for applications demanding immediate results, such as anomaly detection, financial monitoring, and personalized user experiences. However, batch processing remains a dependable choice for periodic, large-scale tasks like report generation, data backups, and complex data transformations.
Choosing between real-time and batch processing is not always straightforward; It depends on your system’s requirements, scalability goals, and operational complexities. Real-time processing ensures low latency for critical tasks, while batch processing optimizes resource use for operations that can tolerate delays. We will explore the strengths and trade-offs of both approaches to make informed decisions for data management strategy.
October 2025 | Blog
What is Event-Driven Processing?
Event-driven processing focuses on a model that responds to events as they occur, triggering actions in real-time based on specific conditions. It enhances responsiveness and scalability by decoupling event producers from consumers, making it ideal for applications like real-time analytics, IoT, and microservices.
Key Features :
- Real-Time Responsiveness: Systems react instantly to events, enabling real-time data processing and decision-making.
- Loose Coupling: Event producers and consumers operate independently, improving system flexibility and scalability.
- Asynchronous Communication: Events are processed asynchronously, allowing systems to handle multiple tasks concurrently without waiting for responses.
- Scalability: Event-driven architectures can scale easily by adding more consumers or producers, accommodating varying workloads.
- Resilience: Decoupled components enhance fault tolerance; if one service fails, others continue to function.
- Event Persistence: Events can be stored for auditing, replay, or recovery, ensuring system reliability and traceability.
Event-driven architecture empowers businesses to build responsive, fault-tolerant, and efficient applications.
For example, financial institutions handle millions of transactions daily, making fraud detection a critical yet challenging task. Event-driven processing enables real-time monitoring and rapid response to suspicious activities. Capturing real-time events from multiple sources—such as payment gateways, ATM withdrawals, or online banking—helps identify anomalies based on predefined patterns or AI models, triggering alerts when suspicious activity is detected.
What is Batch Processing?
Batch processing involves executing tasks on large datasets in groups (or batches) at scheduled intervals rather than in real time. This makes it ideal for back-office operations where efficiency is more important than real-time execution, such as generating reports, processing payroll, or performing system backups.
Key Features:
- Cost Efficiency: Batch processing is cost-effective because it uses resources efficiently by processing data in bulk. Running tasks during off-peak hours helps save on operational costs.
- Simplicity: Batch systems’ infrastructure is relatively simple to set up and maintain. This lack of complexity makes them a go-to choice for many legacy systems and industries that don’t require real-time processing.
- Reliability: By automating large-scale processes, batch systems reduce human error and increase consistency, making them a reliable choice for repetitive, scheduled tasks.
For example, a financial institution doing reconciliation will have to compare transactions from multiple sources, such as bank statements and internal records. Batch processing automates this task by fetching and comparing large datasets at scheduled intervals. Discrepancies are flagged for review, and detailed reports are automatically generated. This approach saves time, reduces human error, and improves accuracy.
Key Differences Between Event-Driven and Batch Processing
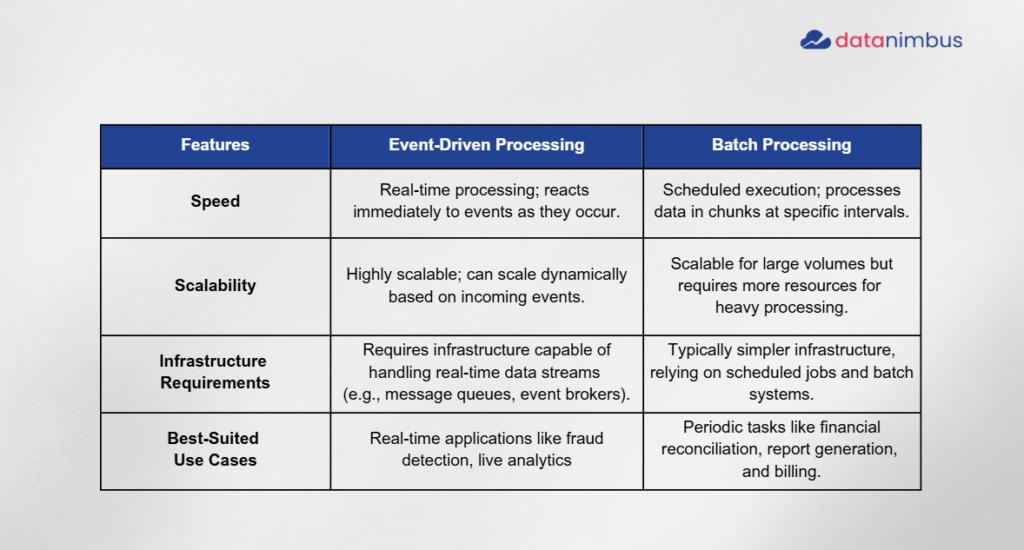
How to Choose the Right Approach for Your Data Platform
1. Nature of Data Flow: Real-Time or Periodic
- Event-Driven Processing: Suited for real-time data flows where immediate action is required. If your system needs to react instantly to events (e.g., fraud detection, IoT data ingestion), event-driven processing is essential.
- Batch Processing: Best for periodic data flows that can tolerate delays. If you process large datasets at scheduled intervals (e.g., monthly billing, payroll), batch processing offers efficiency without the need for constant system updates.
2. Volume of Data
- High Data Volume in Real-Time: Event-driven systems can handle high-throughput data streams but may require advanced infrastructure like message brokers (e.g., Kafka) or event buses. These systems excel when data volume is constant or unpredictable.
- Large, Periodic Data Sets: Batch processing is optimal when dealing with massive datasets that don’t require instant processing. It efficiently processes data in bulk, making it ideal for data warehousing or report generation tasks.
3. System Complexity and Scalability Requirements
- Event-Driven Systems: Highly scalable due to their asynchronous nature. They allow independent scaling of producers and consumers, making them ideal for systems that must grow dynamically with increasing workloads. However, the architecture is often more complex, requiring careful management of message queues, event logs, and microservices.
- Batch Systems: Simpler in terms of design and easier to maintain. While they can scale vertically to handle larger jobs, they are less dynamic. Batch systems are more predictable but less flexible compared to event-driven architectures.
4. Budget and Resource Constraints
- Event-Driven Processing: Real-time systems often require more advanced and expensive infrastructure (e.g., cloud services, event brokers, monitoring tools). The operational costs are higher due to the need for continuous system uptime and the complexity of maintaining a scalable environment.
- Batch Processing: Cost-effective, especially for organizations with budget constraints. By processing tasks during off-peak hours or using minimal resources, batch processing minimizes operational expenses. It’s a good choice for organizations that prioritize cost over real-time processing.






