- AI Platforms
 Fueled by a Visual Designer, Marketplace for Reusable Connectors, ETL & ML Blocks.
Fueled by a Visual Designer, Marketplace for Reusable Connectors, ETL & ML Blocks.
Agentic AI Integrations
Integration enables agents to deliver AI outcomes faster, better, simpler.
DataNimbus FinHub
With the DataNimbus FinHub platform, we offer a whole range of escrow management.Navigate Your AI Journey
Break free from legacy! Modernize your core with intelligent, AI-powered solutions
- AI Applications
- Services

DataNimbus Consulting
- Data AI Strategy
- Data and AI Architecture
- Payment Automation
Product Engineering Services
- Product Design & UX
- Custom APIs
- AI enabled Applications
Data Analytics & AI/ML
- Data Management
- AI Applications and Models
- Custom Workflows

Enterprise Integration
- Custom API
- Process Orchestration
- Intelligent Process Orchestration Management
- Customers
- Resources
- Company
- AI Platforms
 Fueled by a Visual Designer, Marketplace for Reusable Connectors, ETL & ML Blocks.
Fueled by a Visual Designer, Marketplace for Reusable Connectors, ETL & ML Blocks.
Agentic AI Integrations
Integration enables agents to deliver AI outcomes faster, better, simpler.
DataNimbus FinHub
With the DataNimbus FinHub platform, we offer a whole range of escrow management.Navigate Your AI Journey
Break free from legacy! Modernize your core with intelligent, AI-powered solutions
- AI Applications
- Services

DataNimbus Consulting
- Data AI Strategy
- Data and AI Architecture
- Payment Automation

Product Engineering Services
- Product Design & UX
- Custom APIs
- AI enabled Applications

Data Analytics & AI/ML
- Data Management
- AI Applications and Models
- Custom Workflows

Enterprise Integration
- Custom API
- Process Orchestration
- Intelligent Process Orchestration Management
- Customers
- Resources
- Company
- AI Platforms
 Fueled by a Visual Designer, Marketplace for Reusable Connectors, ETL & ML Blocks.
Fueled by a Visual Designer, Marketplace for Reusable Connectors, ETL & ML Blocks.
Agentic AI Integrations
Integration enables agents to deliver AI outcomes faster, better, simpler.
DataNimbus FinHub
With the DataNimbus FinHub platform, we offer a whole range of escrow management.Navigate Your AI Journey
Break free from legacy! Modernize your core with intelligent, AI-powered solutions
- AI Applications
- Services

DataNimbus Consulting
- Data AI Strategy
- Data and AI Architecture
- Payment Automation

Product Engineering Services
- Product Design & UX
- Custom APIs
- AI enabled Applications

Data Analytics & AI/ML
- Data Management
- AI Applications and Models
- Custom Workflows

Enterprise Integration
- Custom API
- Process Orchestration
- Intelligent Process Orchestration Management
- Customers
- Resources
- Company
- AI Platforms
 Fueled by a Visual Designer, Marketplace for Reusable Connectors, ETL & ML Blocks.
Fueled by a Visual Designer, Marketplace for Reusable Connectors, ETL & ML Blocks.
Agentic AI Integrations
Integration enables agents to deliver AI outcomes faster, better, simpler.
DataNimbus FinHub
With the DataNimbus FinHub platform, we offer a whole range of escrow management.Navigate Your AI Journey
Break free from legacy! Modernize your core with intelligent, AI-powered solutions
- AI Applications
- Services

DataNimbus Consulting
- Data AI Strategy
- Data and AI Architecture
- Payment Automation

Product Engineering Services
- Product Design & UX
- Custom APIs
- AI enabled Applications

Data Analytics & AI/ML
- Data Management
- AI Applications and Models
- Custom Workflows

Enterprise Integration
- Custom API
- Process Orchestration
- Intelligent Process Orchestration Management
- Customers
- Resources
- Company
Blog
ETL vs. ELT in the Cloud Era – Why Both Approaches Still Matter
Introduction: Data Integration in a Changing World
In today’s data-driven landscape, choosing the right approach to move and process your data is more critical than ever. Traditional ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) workflows once prevailed when storage was prohibitively expensive, but modern, scalable cloud platforms have led to the rise of ELT (Extract, Load, Transform). This post explores the evolution from ETL to ELT, highlights practical use cases for each, and demonstrates how tools like DataNimbus Designer can integrate the best of both worlds.
October 2025 | Blog
The History: ETL in the Age of Expensive Storage
In the early days of computing, storage was a valuable commodity, making efficient data processing essential. Budgets were tight, and every byte counted. This led to the emergence of ETL (Extract, Transform, Load), which reduced warehouse storage by transforming data upfront.
- Extract data from various sources.
- Transform it into an analysis-ready format (often using dedicated servers).
- Load it into a data warehouse for reporting and insights.
Because transformations happened before loading, data warehouses solely stored well-processed, minimal-volume data. Tools like Informatica, Talend, and DataStage became standard for enterprises, particularly those working with structured data on-premises.
Transition to ELT: Why the Change Was Necessary
As cloud platforms such as AWS, Azure, and GCP have made large-scale data storage much more affordable, the industry needed to adapt to cloud-based solutions. ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) reversed the traditional model:
- Instead of processing data externally, you load raw data first and then transform it at scale using distributed computing engines like Spark, enhancing the data processing capabilities.
- The approach naturally supports unstructured and semi-structured data, aligning perfectly with modern, large-volume workloads in the modern data stack.
With ELT, big data projects can grow without hitting the resource limits of dedicated ETL engines. This shift has allowed organizations to manage streaming data, perform interactive analytics, and integrate various data sources more seamlessly than ever before.
ETL vs ELT: Side-by-Side Comparison
With so much buzz around modern cloud platforms and the rise of ELT Solutions, it begs the question: Is ETL Process truly a thing of the past? Let’s examine the fundamental differences between these approaches to see why each still has its place.
To understand the fundamental differences between ETL and ELT, here’s a brief comparison that emphasizes the unique advantages of each method in the context of data transformation:
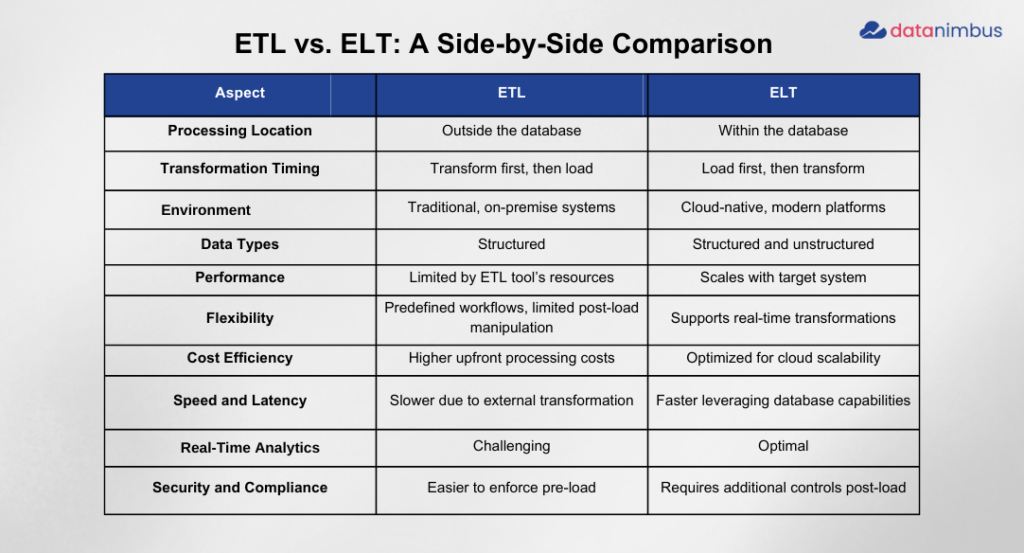
Key Takeaway: Understanding the key differences between ETL and ELT can greatly impact your data strategy. ETL still excels in scenarios where data quality and compliance checks are crucial before data is stored. Conversely, ELT is more suitable for high-volume, flexible, or rapidly changing datasets, especially in cloud environments.
ETL vs. ELT: What Works Best for Which Use Case?
ETL Use Cases
- Regulated Industries (e.g., healthcare or finance) need strict data governance and pre-load transformations to comply with the ETL process.
- Legacy Systems or on-premises environments with limited compute power often struggle with modern data processing needs.
- Consistent schemas are where transformations rarely change, and data volume is relatively stable.
ELT Use Cases
- Large-scale, Cloud-Native ecosystems handling diverse, semi-structured, or unstructured data.
- Real-Time and On-Demand Analytics where quick insight is key.
- High Scalability Needs, such as streaming data pipelines or dynamic reporting dashboards.
The Databricks Perspective and DataNimbus Designer
- Flexibility to manage both ETL and ELT in one place, so you can serve legacy systems and modern data lakes without juggling multiple tools.
- Cloud-Native Integration for smooth transformations within platforms like Databricks.
- Operational Efficiency with built-in automation, monitoring, and streamlined pipeline management.
Conclusion: A Hybrid Future for Data Integration
As data volumes increase and enterprises adopt the cloud, ELT methods will continue to gain momentum due to their scalability and flexibility. However, ETL remains crucial for situations that require stringent quality checks, high compliance levels, or integration with legacy systems.
The bottom line is that the ETL process must evolve to meet modern data requirements: It’s not about permanently selecting one approach; it’s about choosing the right tool for each task. Platforms like Databricks and tools like DataNimbus Designer enable teams to implement a hybrid strategy, blending ETL and ELT techniques to suit each workflow’s specific needs in the modern data stack.
Ready to discover the best of both worlds? Contact us to learn how DataNimbus Designer can future-proof your data pipelines, enhance operational efficiency, and help you derive more value from your data.






